
The accounting equation ensures the balance sheet is balanced, which means the company is recording transactions accurately. This financial statement provides a clear overview of what a company owns, what it owes, and the residual value belonging to its owners. The fundamental accounting equation ensures that total assets reported on the balance sheet always match the combined total of liabilities and equity. The balance sheet serves as a tangible manifestation of this accounting principle, confirming that the company’s financial records are in balance.
Resources

For example, if a business takes out a loan, its liabilities increase, but so do its assets (such as cash or equipment purchased). This process helps maintain balanced balance sheets and keeps the equation balanced. The fundamental accounting equation finds its most direct application in the Balance Sheet, one of the primary financial statements. The Balance Sheet is a detailed representation of the accounting equation at a specific fundamental accounting equation point in time, providing a snapshot of a company’s financial health. It systematically categorizes and presents a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. The purpose of this article is to consider the fundamentals of the accounting equation and to demonstrate how it works when applied to various transactions.
Company Index
Net value refers to the umbrella term that a company can keep after paying off all liabilities, also known as its book value. It specifically highlights the amount of ownership that the business owner(s) has. Almost all businesses use the double-entry accounting system because, truthfully, single-entry is outdated at this point.
Slavery Statement
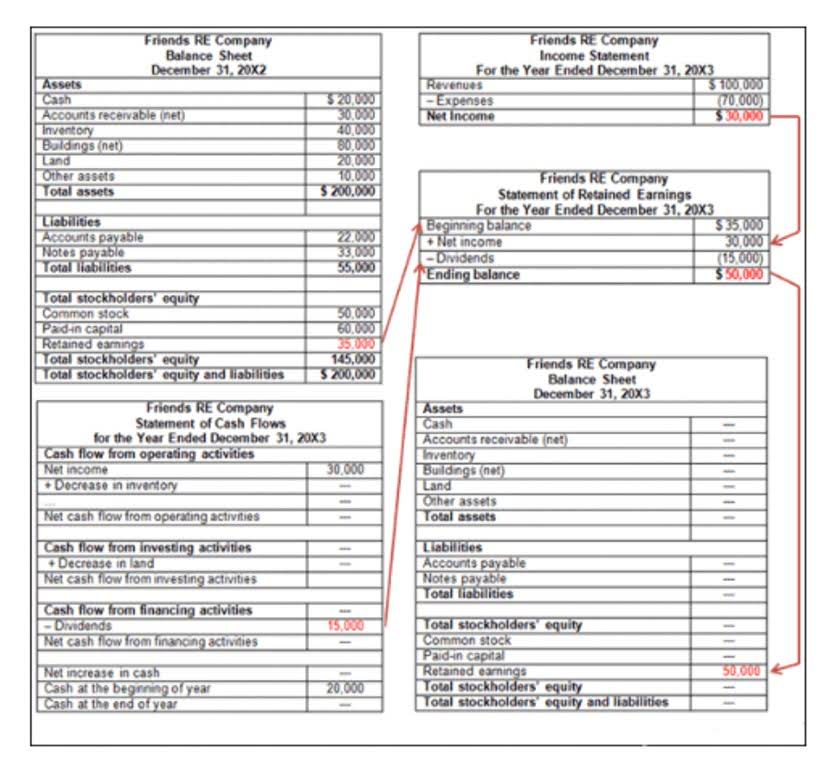
Net income increases retained earnings balance; dividends decrease it. To produce the balance sheet at the end of the period, all transactions are processed for each line item. For a start-up business, the beginning amounts for all accounts are zero. The cumulative impact of all the additions and subtractions gives the ending amount which appears in the balance sheet at the end of the period.
Cash

It is an important financial statement that is a key component of the balance sheet. While the financial landscape continues to evolve and undergo dynamic changes, a key foundational element that continues to guide accounting processes across industries is the accounting equation. Acting as the cornerstone for financial statements, it holds the key in enabling us to understand the financial health of an organization.
- Therefore cash (asset) will reduce by $60 to pay the interest (expense) of $60.
- It’s so much more exciting to focus on product development, marketing strategies, or customer acquisition.
- For example, you can talk about a time you balanced the books for a friend or family member’s small business.
- This is achieved through LiveCube, a ‘No Code’ platform, that replaces Excel and automates data fetching, modeling, analysis, and journal entry proposals.
- The accounting equation is one of the most fundamental concepts in accounting.
Liabilities
- All transactions are recorded by the accounting system and used to produce an income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement.
- With 200+ LiveCube agents automating over 60% of close tasks and real-time anomaly detection powered by 15+ ML models, it delivers continuous close and guaranteed outcomes—cutting through the AI hype.
- Costs can include rent, taxes, utilities, salaries, wages, and dividends payable.
- This is precisely where fractional, interim, and virtual CFO services deliver exceptional value.
- The balance of the total assets after considering all of the above transactions amounts to $36,450.
- The monthly payment of rent to a landlord, the purchase of equipment from a supplier, and the sale of goods to customers are all examples of external transactions.
- Some also confuse the equation’s simplicity with a lack of importance, overlooking its crucial role in preventing errors and providing a clear financial snapshot.
All the entries made to the debit side of a balance sheet should have a corresponding credit entry on the balance sheet. For example, if a company buys a $1,000 piece of equipment on credit, that $1,000 is an increase in liabilities (the company must pay it back) but also an increase in assets. This equation holds true for all business activities and transactions. If assets increase, either liabilities or owner’s equity must increase to balance accounting out the equation. Current liabilities are obligations that a company needs to settle within one year. Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due in more than one year, such as long-term loans and bonds payable.
- Let’s walk through some simple examples to see how the equation works in common scenarios.
- This opportunity to provide a service or realize potential economic gain for the company will ultimately result in cash inflows (also known as receipts).
- As you can see, all of these transactions always balance out the accounting equation.
- Working capital indicates whether a company will have the money needed to pay its bills and other obligations when they are due.
- For a start-up business, the beginning amounts for all accounts are zero.
- This inherent balance is not merely a formatting convention but a foundational check, ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial reporting.
- Liabilities are debts that a company owes and costs that it must pay to keep running.
- It’s easy to overlook liabilities that haven’t been paid yet, like wages payable or accrued interest.
- When discussing equity, it is essential to differentiate between revenues and expenses.
- Like assets, we can classify liabilities into current and non-current liabilities.
These may include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bond issues, warranties, and accrued expenses. The balance sheet always balances out but the accounting equation can’t tell investors how well a company is performing. Following are the accounting transactions relating to Mr. P’s business. Use the accounting equation to show their effect on gym bookkeeping his assets, liabilities and capital.




